 ).
).
THE HOMEOBOX PAGE |
On this page I try
to maintain information relevant to homeobox genes
(in particular about classification/evolution). Should you find any of
this information out of date or wrong, or if you simply want to add
some
information, please send me an email ( ).
).
This page and all
figures are Copyright by Thomas R. Bürglin
"The homeobox was
originally described as a conserved DNA motif of about
180 base pairs. The protein domain encoded by the homeobox, the
homeodomain,
is thus about 60 amino acids long. The first genes found to encode
homeodomain
proteins were Drosophila developmental control genes, in particular
homeotic
genes, from which the name "homeo"box was derived. However, many
homeobox
genes are not homeotic genes; the homeobox is a sequence motif, while
"homeotic"
is a functional description for genes that cause homeotic
transformations."
These excerpts were taken from Bürglin, T.R. (1996) Homeodomain Proteins. In Meyers, R.A. (ed.), Encyclopedia of Molecular Biology and Molecular Medicine, Vol 3., VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Weinheim, pp. 55-76.
Thus, in
summary one can say that the homeodomain is a DNA-binding domain that
occurs in proteins that are usually transcription factors. These
transcription factors regulate the transcription of other genes and
hence very frequently play important roles in development of
multicellular organisms.
Some definitions
Hox genes:
Hox genes are a subgroup of homeobox genes. In vertebrates these genes
are found in gene clusters on the chromosomes. In mammals four such
clusters exist, called Hox clusters. The gene name "Hox" has been
restricted to name Hox cluster genes in vertebrates.
Only genes in the HOX cluster should be named Hox genes. So note:
homeobox genes are NOT Hox genes, Hox genes are a subset of homeobox
genes.
HOX cluster:
The term Hox cluster refers to a group of clustered homeobox genes,
named Hox genes in vertebrates, that play important roles in pattern
formation along the anterior-posterior body axis. In fact, the first
homeobox genes discovered where those of the Drosophila homeotic gene
clusters, i.e. the "Antennapedia complex" and the "Bithorax complex",
which summarily are referred to as HOM-C (homeotic complex). This HOM-C
complex in Drosophila is the evolutionary homolog of the vertebrate Hox
clusters and the evolutionarily related homeobox gene clusters in other
animals (i.e. chordates, insects, nematodes, etc.) are now also called
HOX clusters.
homeodomain: a DNA-binding domain,
usually about 60 amino acids in length, encoded by the homeobox.
homeobox: a fragment of DNA of about
180 basepairs (not counting introns), found in homeobox genes.
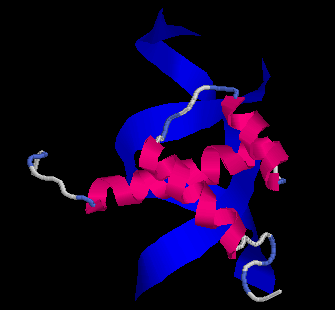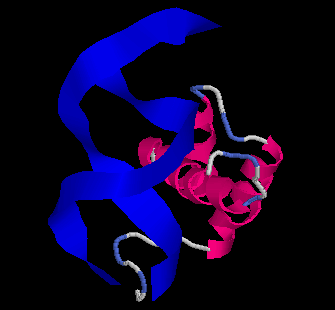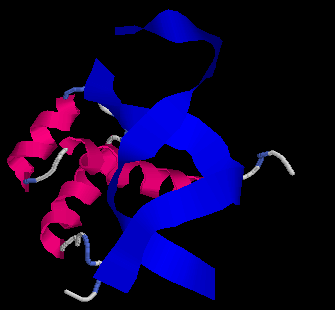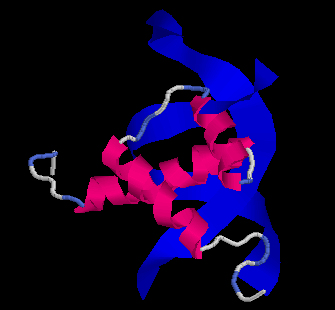
The Evolution of Homeobox genes. Bürglin, T.R. (1995) in 'Biodiversity and Evolution', Arai, R., Kato, M., Doi, Y. (eds.), The National Science Museum Foundation, Tokyo, pp. 291-336, ISBN 4-9900433-0-8, The National Science Museum Foundation, 7-20 Ueno Park, Taito-ku, Tokyo 110, Japan.
Analysis of TALE superclass homeobox genes (MEIS, PBC, KNOX, Iroquois, TGIF) reveals a novel domain conserved between plants and animals. Bürglin, T.R. (1997) Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 4173-4180.
The PBC domain
contains a MEINOX domain:
Coevolution of Hox and TALE homeobox genes? Bürglin, T. R.
(1998). Dev. Genes. Evol., 208,
113-116.
Some families in the prd-like class have conserved motifs upstream of the homeodomain (e.g., ceh-10). Svendsen, P. C., and McGhee, J. D. (1995). The C. elegans neuronally expressed homeobox gene ceh-10 is closely related to genes expressed in the vertebrate eye. Develoment 121, 1253-1262. Brand new class: a sea urchin homologue for C. elegans ceh-19 has been found. Popodi, E., Andrews, M. E., and Raff, R. A. (1995). A sea urchin homologue of ceh-19, an unusual homeobox-containing gene from a nematode. Gene 164, 367-368. E. Popodi suggest ceh19 as class name. Structure of the LIM domain protein CRP determined: Perez-Alvarado et al., 1994. Nature Struct. Biol., 1, 388ff. New class: bsh class (bsh = brain-specific homeobox, Drosophila), due to a C. elegans homologue. Nomenclature change: XlHbox8, mouse ipf-1, rat idx-1 and stf-1 (I guess they must be the same) have undergone a name change, which is approved by the International Mouse Nomenclature Committee. These genes are now all called pdx-1 (C.V.E Wright, pers. comm.). (I hope XlHbox8 is indeed pdx-1, and not a future pdx-2...). The name of this family is still the Xlox family. A novel small conserved domain is found between mouse Sax1 and Drosophila NK-1/S59 upstream of the homeodomain. Smith, S. T., and Jaynes, J. B. (1996). A conserved region of engrailed, shared among all en-, gsc-, Nk1-, Nk2- and msh-class homeoproteins, mediates active transcriptional repression in vivo. Development 122, 3141-3150. It seems more and more likely that the plant (so far mainly Arabidopsis) genes Athb-x/HATx cannot be assigned to any particular animal homeobox gene class. Thus, this group of genes is grouped into its own class, the HD-ZIP class. New class of homeobox genes, resulting from genes sequenced by the C. elegans genome project: Prh class (77% identity vertebrate - C. elegans). A new class, the Bar class, is formed by C. elegans genes and the Drosophila BarH genes (aka OM) (77% identity between C. elegans and Drosophila). The vertebrate gene Barx1, as well as the Xom = Xvent = Xbra = Vox genes have affinities to the Bar genes, althought they do not seem to be direct vertebrate orthologues. Xnot class: Xnot, zebrafish floating head, and a Drosophila gene (90Bre) form a new class. This class seems to have affinities to the ems class. The Ptx1 = P-OTX gene (Lamonerie et al., 1996, Genes Dev. 10, 1284; Szeto et al., 1996 PNAS 93, 7706) is an orthologue of the C. elegans gene unc-30 (thus P-Otx is a misnomer), a very divergent member of the prd-like class. They form their own family, Ptx.
Sacharamyces cerevisiae
Encephalitozoon
cuniculi (Microsporidia)
Under construction:
Arabidopsis
thaliana
(plant) homeobox gene list table and supplementary material
C. elegans homeobox genes
Nomenclature of vertebrate HOX cluster genes, listed with old names and accession numbers as in SwissProt. Hox gene list.Some older overviews and reviews:
- Kappen, C., Schughart, K., Ruddle, F.H. (1993) Early evolutionary origin of major homeodomain sequence classes. Genomics, 18, 54-70.
- Scott, M.P., Tamkun, J.W., Hartzell III, G.W. (1989) The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biophys Acta, 989, 25-48.
- Gehring, W.J., Affolter, M., Bürglin, T.R. (1994) Homeodomain proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 63, 487-526.
- Review of LIM domain proteins: Dawid et al., 1995, LIM domain proteins, C.R.Acad.Sci. Paris Sciences de la vie, 318, 295-306.
- A good overview over the NK-2 class homeobox genes: Harvey, R. P.(1996). NK-2 homeobox genes and heart development. Dev. Biol. 178, 203-216.
- Spaniol, P., Bornmann, C., Hauptmann, G., Gerster, T. (1996). Class III POU genes of zebrafish are predominantly expressed in the central nervous system. Nucl. Acids. Res. 24, 4874-4881.
From the 1995 Homeobox Workshop in Monte Verita in Ascona, Switzerland.
The group photofrom the workshop, signed by Ed Lewis.
Two more pictures of Ed Lewis on the evening of the Nobel Prize announcement (from left to right):
Meera Berry and Ed Lewis, and Walter Gehring, Ed Lewis and the Manager of Monte Verita.
Search of PUBMED with the keyword "homeobox". For structural views of homeodomain proteins, go to the RCSB PDB Protein Data Bank and search with the term "homeo*", or other terms such as e.g., "POU". You can look at structures on that Web site, or download the structures to view them in programs such as RasMol. Gehring lab home page, with more pictures on homeobox genes. Homeobox proteins, automatic alignments. HOX-pro-Network of Vertebrate Homeobox Genes, including Promoter Regions Analysis Pages. HOX Pro db, Homeobox genes database (much faster link than above) CRP antibody products, have anti-homeobox antibodies. Search for homeobox genes in the worm breeders gazette (WBG). The Hox database